Governance and Risk Management
At GAIL, we believe that an effective and strong governance framework has the capability to exercise efficient practices while managing risks that are crucial for our business. Managing risk is a systematic process of identifying, analyzing and addressing a company’s risks and taking actions to protect the business. The governance framework at GAIL can address the potential risks and can deliver constructive feedbacks and evaluations to align the management responsibilities with the board’s oversight of the organization. To improve GAIL’s corporate governance framework, we periodically review and update our organizational policies and practices.
Governance Structure
The Board of Directors remains at the top of the governance structure, inclusive of the shareholders and multiple committees of the board. GAIL has a unitary board structure, which is governed by a formal Board Charter that sets out the composition of the Board, its responsibilities and the process of selection of its members. The Directors on the Board are nominated/ appointed by the Government of India. As on 14th August 2020 there are a total of 9 members in the board, that comprise of 04 Functional Directors including the Chairman and the Managing Director, and 5 Non- Executive Directors (comprising 02 Government Nominee Directors, and 03 Independent Directors). The average tenure of the Board member is 04 years. Further details pertaining to the composition and profiles of the Board members are available on our website.
The Board of Directors oversees the organizational management to assure that all the stakeholder demands/needs are met promptly. By responsibly addressing the concerns of the stakeholders in our value chain, the Board of Directors and the senior management team ensure that the longterm interests of multiple parties are recognized. The thoughtfully crafted induction and orientation programs assist the newly appointed directors to understand the system better, while enabling them to contribute towards the holistic organizational growth. The welcome kit provided to them during the induction period contains the detail of their roles and responsibilities, including the legal and regulatory policies they may be obligated to follow. To enhance and upgrade the skill and expertise of the Board Members, we provide them with adequate training based on our training policy. As a part of this policy, the board members including the directors are often nominated to participate in conferences on industry matters organized by parties such as the Department of Public Enterprise (DPE), Standing Conference of Public Enterprises (SCOPE), and other reputed Institutes.
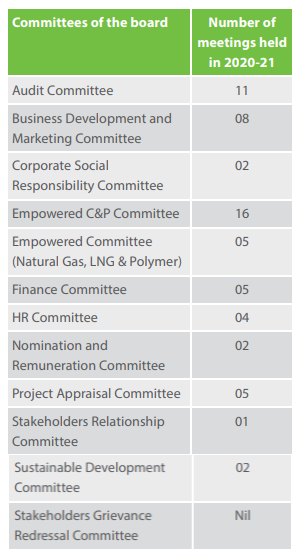
Committees of the Board
The governance structure of GAIL is composed of 12 sub-committees of GAIL’s Board. Since each committee carries out specific functions, the well-defined terms-of-reference enable them to function efficiently, including the swift resolution of concerns. The combination of independent and non-independent directors in each committee not only brings diversity but also enables the board to be fair and just in their deliberations. While the board works on their pre-defined strategic focus areas, it is committed to set its targets to improve the operations throughout the year. The Board of Directors assesses and reviews the functioning of the committees, in addition to periodically reviewing the targets and goals of the team.
Performance Evaluation, Remuneration and Incentives
Being a Public Sector Enterprise, the members of the Board are appointed and evaluated by the Government of India. The performance evaluation of members of the Board is done on both financial and non-financial parameters as prescribed in the MoU between GAIL and Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoPNG). The variable pay bracket for Directors is determined annually based on the composite score thus obtained. The performance evaluation of the top management including CMD, Directors, EDs and GMs consist of parametric scoring of the individual based on business, financial, CSR, human resource, and R&D performance of the GAIL during the reporting period.
The average salaries of female employees at the management and non-management level are INR 1,21,430 and INR 50,422 while the same for male employees at the executive and management levels are INR 2,66,554 and INR 1,47,721 respectively. The vesting period for CMD compensation is 5 years or date of superannuation, whichever is earlier. The ratios (average female salary to average male salary) of the management and non-management levels are 0.82 and 0.92. During this reporting year, GAIL experienced no delay in the payment of wages to the employees. Payments are processed promptly based on the determined pay cycle
The percentage increase (from FY 18-19 to FY 19-20) in annual total compensation for the organization’s highest-paid individual is 13.11. The Median percentage increase (from FY 18-19 to FY 19-20) in annual total compensation for all the employees (excluding the highest-paid individual) is 6.64%. The ratio of the annual total compensation for the organization’s highest-paid individual to the median annual total compensation for all the employees (excluding the highest-paid individual) Is 2.58
GAIL has achieved ‘Excellent’ MoU rating for the financial year 2018-19 with a score of 92.76. MoU for the FY 19-20 was signed between the Chairman and the Managing Director, GAIL and Secretary (P&NG), Government of India on 30th May 2019.
In 2019-20, GAIL’s MoU was aligned with GOI’s aspiring vision of transforming India into a Gas based economy. The key thrust area of MoU was mainly on continuing the effort to increase the number of PNG connections and CNG stations. Other critical aspects were related to the key financial parameters, gas marketing, gas transmission, project implementation, capital expenditure and as well as the support given by your company to StartUps to align with GoI’s vision of ‘Start-Up India’.
GAIL has made earnest efforts in fulfilling MoU obligations despite adverse effects faced due to the COVID-19 situation. Self-evaluation of MoU FY 19-20 will be carried out and submitted to DPE in due time, the result of which is expected to be announced by December 2020. The compensation related to the performance is assessed based on the performance evaluation score and the composite score. Highlights related to the remuneration are provided below:
Highlights of Remuneration and Incentives at GAIL
- In FY19-20,the total compensation ofthe CEO/ CMD was INR 91.17 lakh (w.r.t. 14/02/2020)
- n FY 19-20, the median compensation of all the employees (except CEO/CMD) was INR 3206318.08
- In FY 19-20, the mean compensation of all the employees (except CEO/CMD) was INR 3721984.60
- The ratio between the CEO’s annual compensation and the median of all employees’ compensation is 3.24039
- The ratio between the CEO’s annual compensation and the mean of all the employees’ compensation is 2.79144
Avoidance of Conflict of Interest
We strive to create a culture of ethics and trust by setting the right tone at the top. We are promoting transparency and accountability amongst all our stakeholders to ensure that there are no possible ways of conflict of interest in workforce operations. Besides, we are creating a trustworthy environment in which the employees are not afraid to bring up and disclose their conflicts of interest; and to properly manage such issues and concerns, a board-level deliberation is carried out. GAIL policies on conflict of interest are provided next:
- In case a director is directly or indirectly interested in a particular agenda/matter, they abstain themselves from participation in the discussion of such an agenda.
- Each director gives the disclosure of his interest in any company’s or body’s corporate firm, or other association of individuals by giving a notice in writing ;and the same is put up to the board.
- The Related Party Transaction Policy at GAIL enables us to deal with all the issues and concerns raised on related party transactions. This policy follows requirements set by the SEBI (LODR) Regulations, 2015 and The Companies Act, 2013. Additionally, it comprises materiality policies and guidelines for managing related party transactions. Our annual Sustainability Report is the medium, through which we disclose our issues pertaining to the conflict of interest. The quarterly GAIL Corporate Governance Report provides disclosure of all conflict of interest cases related to our stakeholders.
Internal Control System and their Adequacy
We have developed promising guidelines, frameworks, and policies as a part of our internal control system in order to strengthen operational and financial integrity.
Improved controls over the financial reporting process help in developing more accurate and reliable financial statements and make audits more comprehensive. GAIL’s Internal Financial Control System (IFC) is useful in developing an updated formal, centralized, and managed internal financial control documentation for the company. A Risk Control Matrix (RCM) was formed in consultation with external consultants after the IFC compliance study.
Audit Committees play a critical role in overseeing internal control. Our internal audit team provides advice and recommendations on the potential gaps and risks, including potential efficiencies and enhancements to business and processes. The professionally qualified audit team members have an academic and professional background in accounting, IT, and engineering. This team assesses the risk management system and reports the same to the audit committee. The audit committee of the board is responsible for approving the annual audit program and reviews the findings of the audit team and the CAG audit. Promoters’ audit of subsidiaries, joint ventures, and E and P blocks are also carried out by the internal audit team.
Ethics and Integrity
We are committed to conducting business, using the highest ethical standards; and GAIL’s code of conduct is designed to further that commitment. Our business processes and practices are directed to achieving excellence while managing issues related to the environment, health and safety, human rights, etc.
GAIL’s Code of Conduct and related circulars set forth our values, principles, and rules on which we base our operations. We develop and enable sustainable growth and build relationships of trust with our clients, employees, and business partners. Employees including senior management and board members, contractors, and all company representatives are required to follow this code of conduct policy mandatorily.
We, as a responsible corporate citizen, including our subsidiaries, comply with anti-corruption, antiboycott, export control, and trade sanctions laws across our sites. In FY 19-20, 1.6% of employees received training on anti-corruption policies and other organizational procedures.
Our strong policy frameworks enable us to grow our business sustainably and safeguard us against corruption and other unethical activities. Our organizational policies are provided below
- Code of Conduct, Discipline and Appeal (CDA) Rules/Standing Orders
- Fraud Prevention Policy
- Whistle Blower Policy
- Code of Fair Disclosure and Conduct
- Code of Conduct to Regulate, Monitor and Report Trading by Insiders
- Code ofConductforBoardMembers andSenior Management Personnel
We have also incorporated a policy for the determination of materiality disclosure for timely disclosure of our material concerns to our stakeholders. This policy is in accordance with Regulation 30 of SEBI LODR, 2015.
We conduct awareness workshops periodically to ensure that our organization is 100% corruptionfree and our employees and suppliers are committed to fighting corruption. Additionally, we undergo periodic risk assessments to identify the risks related to corruption in our operational units. During FY 19-20, GAIL received zero corruptionrelated cases and no significant risk of corruption was identified and reported through this risk assessment process.
The Right To Information, Whistle Blower Policy, Fraud Prevention Policy and the Integrity Pact encourage employees to report, in good faith, any suspicious, illegal, unethical, or inappropriate activities undergoing in the organization. It helps strengthen the organization against corruption and make the vigilance system more robust.
Governance Mechanisms
Right to Information:
In order to promote transparency and accountability, an appropriate mechanism has been set up across the Company in line with the provisions of the Right to Information Act, 2005. We have nominated CPIO/ACPIOs/ Appellate Authorities at our units/ offi ces across the company to provide information to the citizens under the provisions of the RTI Act. GAIL has hosted RTI Guidelines and related information on its website and these may be accessed at htt p://www.GAILonline.com/fi nal_site/RTI.html Besides, MIS Report on RTI Applications, Record Retention Schedule and latest RTI Audit Report have also been hosted under the same link.
In FY 19-20, the total RTI applications received were 768, out of which 763 applications were successfully disposed of. Around 19 applications were fi led by GAIL employees among all the RTI applications received. 102 fi rst appeals were made from the applications that were disposed of; in that, 100 appeals were successfully disposed of. About 14 applications went through the Central Information Commission (CIC) hearing for resolution.
Whistle Blower Policy:
We encourage our employees, who have concerns about the suspected misconduct to come forward and express their concerns without fear. This policy aims to provide a confi dential platform for the employees to raise concerns without being victimized or being harassed in any manner.
Fraud Prevention Policy:
This policy is put in place for detection, prevention, and reporting of frauds or suspected frauds/fraudulent activities at GAIL. It applies to frauds or suspected frauds in connection with the business transaction(s) with GAIL committ ed by employee(s), exemployee(s) working as an advisor(s), the person engaged on ad-hoc/temporary/contract basis, vendor(s), supplier(s), the contractor(s), the customer (s), lender(s), consultant(s), the service provider(s), any outside agency(ies) or their representative(s), employees of such agencies, and/or any other parties.
Related Party Transaction:
In line with the requirement of Regulation 23 of SEBI LODR, 2015 and the Companies Act, 2013, the audit committ ee of GAIL quarterly reviews the details of related party transactions. Approval of the audit committ ee/or board/or shareholders, as required, is taken for the related party transactions. Initiatives such as e-tendering, e-payments, bill watch system, etc. have been put in place to improve transparency in the system.
Anti-corruption:
GAIL strongly upholds the guidelines and circulars of the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) for dealing with issues related to ethics, bribery and corruption at the organization level. The policy applies to GAIL and its subsidiaries as well as in Joint Ventures , having jurisdiction of GAIL Vigilance Department. To sensitize stakeholders of GAIL against corruption, an annual vigilance awareness week is also organized
Vigilance Initiatives at GAIL
Guidelines and circulars of the Central Vigilance Commission are followed while dealing with issues related to ethics, bribery and corruption at GAIL and its subsidiaries as well as in joint ventures (JVs) having jurisdiction of the GAIL Vigilance Department.
In order to ensure transparency, equity and competitiveness in procurement, GAIL has adopted the provision of Integrity Pact in its tenders of value more than INR 1 crore for works and undertaken procurement of goods and services as recommended by the Central Vigilance Commission. Dr Meeran Chadha Borwankar, IPS (Retd), Mr. Ajit Mohan Sharan, IAS (Retd.) and Mr. Sanjeev Bihari, IRS (Retd.) have been appointed as Independent External Monitors for looking into complaints as per the provision of the integrity pact.
GAIL Vigilance Department carries out regular surprise checks, periodic inspections, and examination of CAG /internal audit paras for the detection of vigilance angles, if any. Various system improvements have been undertaken to ensure greater transparency and automation of processes for reducing manual intervention. Review of policies and procedures have also been carried out, which can help in the reduction of corruption and ensure all-round good governance. To spread vigilance awareness and to address grievances; vendor meets, customer interactive meets, vigilance awareness workshops/sensitization programs, and engineer-in-charge coaching are held periodically for all the stakeholders
During the period, based on the investigations of the cases, the following system improvements have been implemented:
To ensure greater transparency, additional information viz Health and Safety Policy, Information Security Policy, Quality Policy and Risk Management Policy have been displayed on GAIL website. In addition, the list of parties/ vendors banned/ put on holiday by GAIL is also being displayed on GAIL’s website.
In order to have uniformity in the tender conditions for submission of EMD & CPBG in the form of DD / Bank Guarantee being submitted by the bidder/ Vendor, provisions have been made that EMD and CPBG will not be accepted in case the same has to reference of remitter/financer other than bidder on the aforementioned financial instrument of EMD/ CPBG.
To avoid the time gap between the date of complaint uploaded by the complainant in the Online Complaint system on GAIL’s website and the date when Complaint system is accessed by Vigilance Executive, provision for generating auto e-mail alerts has been developed. In FY 19-20, we received 111 complaints under vigilance, 97 complaints were successfully concluded.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism
Our stakeholder responses and concerns are two of our top priorities. The grievance redressal mechanism allows reception and redressal of complaints or grievances by our stakeholders, enabling prompt actions on any issue raised by them, thus allowing for better services. We have developed an online grievance redressal forum named ‘Samadhan’ that is accessible to all of our stakeholders to raise their concerns. Complaints on vigilance, a blatant violation of systems and corruption, forgery, cheating, misappropriation, favours, willful negligence, reckless decision making, procedures, and irregularities in the exercise of delegated power can be raised and resolved through our online portal: http://GAILonline. com/ onlineComplants.html
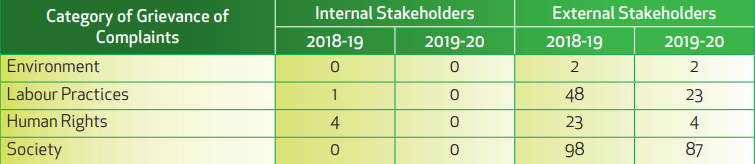
All the written complaints received from all workplaces and centres are uploaded to the Centralized Public Grievance Redressal and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS), which is accessible to all the citizens, who have lodged this complaint. CPGRAMS is a Government of India Portal, aimed at providing the citizens with a platform for redress of their grievances. Complaints are directly received by the MoPNG. During FY 2019-20, a total of 116 public grievances through centralized public grievance redress and monitoring system (CPGRAMS) were received during the reporting period.
Grievance/Complaints received through CPGRAMS
Risk Management
Risk Management is an ongoing process of identifying, analyzing, and managing risks within all the operational units of GAIL. While we adhere to all the standards and keep pace with our industry peers, we map and manage both financial and non-financial risks through Enterprise Risk Management.
Risk assessment of several factors (climate change, fuel prices, energy supply security, etc.) that could potentially influence our business growth is studied and analyzed through Enterprise Risk Management. As a part of the process, the risk management plan includes business continuity planning, risk communication, resource allocation, etc.
Overarching Management Approach
Our comprehensive policy framework such as the risk management policy is deployed on both the corporate and business levels by our committed and independent Risk Management department to improve our approach to managing risks to meet the demands of an evolving business environment. The risk management policy enables us to take proactive measures to review, report, and mitigate risks at our organization while contributing to the sustainable business growth.
The Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework provides an integrated framework to periodically review the organizational risks by the boards by providing an objective view of the overall control system that leads to the overall risk management at GAIL. Additionally, it provides a deeper understanding of the possibilities for the improvement in businesses practices related to the operations.
The ERM has been rolled out across the organization including zonal marketing offices. The highest governance body in reviewing the effectiveness of GAIL’s risk management processes is the Board of Directors. The board, through the Audit Committee, Risk Management Committee, Corporate Level Risk Steering Committee oversees the establishment and implementation of an adequate system of risk management across the organization. The site-level risk steering committee chairman and Corporate Level Risk Steering Committee review various types of risks whether existing and anticipated in the short, medium and long-term. Risk Management Department apprises the Corporate Level Risk Steering Committee (CLRSC) of executive directors chaired by the Director (BD) quarterly, RMC of functional directors chaired by the Director (Marketing) annually and Audit Committee annually and the Board annually.
Unit level risks including social and environmental risks are mapped and monitored quarterly through Site/Unit level Risk Steering Committee headed by unit OICs/function heads. Mitigation measures are also devised and monitored by the respective units. GAIL has identified top corporate risks, which include market, strategic, JV subsidiary and the financial Risks.
Risk Management and Strategic Initiatives
GAIL’s effective risk management facilitates and initiatives enable us to achieve our organization’s objectives and safeguard operations while complying with legal, regulatory, and societal expectations. By managing risks, GAIL is enhancing our capabilities to better respond and adapt to the changing environment. Risk management involves a 6-step process consisting of 1. Scope, Context, Criteria 2. Risk Assessment (Identification, Analysis and Evaluation) 3. Risk Treatment 4. Recording and Reporting. 5. Monitoring and Review 6. Communication and Consultation. This process helps oversee the strategic direction and management of business operations, including effective management of risks. Review report of risk register is submitted by the unit risk owners quarterly by the 10th day of following the quarter-end, and a risk database review report is submitted annually by the 45th day following the financial year-end through risk management online RMS.
Specific group of GAIL namely HSE coordinate all the risks pertaining to environment and safety. CSR group coordinate all risks pertaining to social and CSR. These groups have to ensure all the current and expected risk exposures. Environmental, Economical and Social. Risks are identified (qualitatively and quantitatively), evaluated, analyzed and appropriately managed by placing effective mitigation plans. Both groups update Management from time to time.
Key Risks and Mitigation Measures
Some risks are easier to manage, while others often require an adequate amount of time. Hence, it is difficult to bind risks in terms of the financial year. GAIL Corporate Level Risk Steering Committee has identified risks and mitigation actions to improve the operational performance. We are taking appropriate action to resolve/ deliberate the identified risks. Top ten corporate level key risks are as under:
- Key Risks: Market risk of LNG, linked with
Henry Hub (HH), in case of adverse movement
of crude oil price, continuously suppressed spot
LNG prices and expected to increase in domestic
gas availability
Mitigation Measures :
- Market risk has been largely mitigated for the year 2019 to 2020 by various measures such as destination swap of LNG volumes, sale in international markets, time swap and hedging
- Efforts for mitigating the risk from the year 2021 onwards are under progress by way of ramping up of marketing of LNG volumes in domestic market and efforts to sell LNG in international markets from time to time based on the market conditions
- The US volume risk (LNG) will be largely mitigated after 2028 onwards, as the LTRLNG contract with PLL will expire
- GAIL has also executed long term GSA with anchor sector customers of approximately 11 MMSCMD (with upcoming fertilizer unit), which will be serviced through HH volumes; this has significantly reduced the volume risk on account of HH volumes
- Key Risks:Risk emanating out of GAIL’s
comfort letter to bank for providing PBG (INR
5200 crore) to GAIL Gas Ltd. {Wholly owned
subsidiary of GAIL (India) Limited} for Bengaluru
CGD project.
Mitigation Measures :
- Committed MWP target with PNGRB for pipeline laying and PNG connections is already achieved
- Key Risks: Risk of reduction in the margin of
petrochemical due to lower industry demand,
lower sale price and high input cost
Mitigation Measures :
- Proper coordination with production plant for the production of marketable grades
- Proper coordination with zonal offices/ CS and aggressive marketing to ensure enhanced polymer sale and profitability
- Expansion of market by export measures to liquidate surplus inventory
- Optimization of feedstock and conversion cost
- Key Risks:Risk of delay in project execution
due to delay in obtaining Right of Use (RoU)/land
Mitigation Measures :
- Liaison with state and district administration
- Permanent land acquisition through government procedure and direct negotiation with farmers/landowners is in place
- Timely submission of application and regular follow-up with concerned stakeholders
- Initiation of welfare activities for the projectaffected areas
- Key Risks: Risk of underutilization of pipeline
due to sluggish growth in gas energy consumption
Mitigation Measures :
- Availability of more customer-friendly and flexible GTA/ GSA for the benefit of small customers
- Development of framework agreement for deferred delivery services on gas transportation
- Approval of guidelines on “Amicable settlement of disputes with consumers/ shippers under Gas Transportation Agreement” applicable for small shippers up to 0.1 MMSCMD
- Facilitation in online NG capacity booking through the website for prospective customers
- Discussion with shippers for capacity booking
- Synchronization & prioritization of CGD bidding along with the upcoming or in place pipelines with PNGRB/MoPNG
- Increase in customer interaction
- Expedition of last-mile connectivity initiatives
- Key Risks: Major LPG Leakage in RT/SV
stations/LPG pipeline
Mitigation Measures :
- Monitor health and integrity of pipeline regularly in line with the Integrity Management System (IMS)
- Monitor pipeline leakage by online Leak Detection System (LDS) functionality of APPS implemented
- Detection of pipeline intrusion through Pipeline Intrusion Detection System (PIDS): GAIL has implemented Pipeline Intrusion Detection System (PIDS) in some stretch of JLPL Loni section and VSPL pipeline Vizag section on a pilot project basis
- Review of Emergency Response and Disaster Management Plan (ERDMP) and Evacuation Standard Operating Procedure (ESOP), which have been put in place for the handling of emergency during LPG leakage
- Management through hot/mobile flare system in (JLPL and VSPL)
- Key Risks: Risk of third-party damage and
encroachment in pipelines
Mitigation Measures :
- Removal of encroachment from RoU/land
- Increase in ROU surveillance through air or foot patrolling as per the required frequency
- Close coordination with municipal corporation/development authorities
- Display of warning/safety boards at vulnerable locations
- Regular follow up with encroachers, district authority by sites
- Communicate to concerned authorities for helping in encroachment free RoU
- Implementation of PIDS and drone -trial completed
- Key Risks:Risk of statutory/regulatory noncompliance
Mitigation Measures :
- Required response by the concerned department and follow up with concerned authorities
- Key Risks:Risk of unfavorable regulatory
changes.
Mitigation Measures :
- Appeal to PNGRB and rigorous follow up
- Interaction with the regulatory body and advocacy
- Key Risks:Risk on further investment in RGPPL/KLL.
- Breakwater job awarded in February 2020 with a completion period of 30 months to make it all-weather terminal and de-risking